Excel's
sorting and filtering capabilities are vital tools that empower users to manage
and analyze large datasets with ease. Sorting allows you to arrange data in a
meaningful order, while filtering lets you narrow down data to view only the
information that meets specific criteria. In this SEO-optimized blog, we'll
explore the intricacies of sorting and filtering data in Excel, empowering you
to efficiently organize, analyze, and gain valuable insights from your
datasets. Let's dive into the world of data management with Excel!
Understanding
Sorting in Excel:
Sorting data
in Excel helps you organize information in ascending or descending order based
on a selected column. This feature is particularly useful when you have large
datasets, and you want to identify trends or find specific values quickly.
To sort
data in Excel, follow these steps:
a. Select the range of cells that you
want to sort.
b. Navigate to the "Data" tab
on the Excel Ribbon.
c. Click on the "Sort" button
to open the sorting options.
d. Choose the column by which you want
to sort the data.
e. Select the sort order (ascending or
descending).
f. Click "OK" to apply the
sorting.
For
example, if you have
a dataset with sales figures, you can sort the data in descending order to
quickly identify the highest sales values.
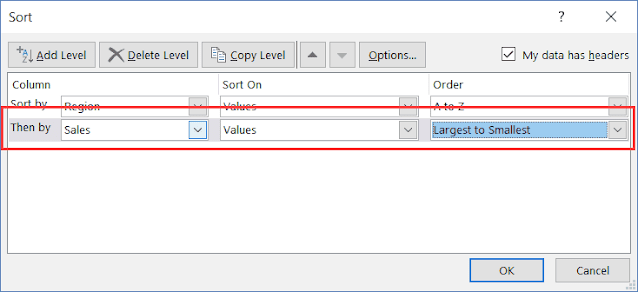
Sorting
Data with Multiple Levels:
Excel allows
you to sort data with multiple levels, which is incredibly valuable when you
need to sort data based on more than one criterion. For instance, you might
want to sort sales data first by region and then by product category to gain a
deeper understanding of sales performance.
To sort
data with multiple levels:
a. Select the range of cells you want
to sort.
b. Navigate to the "Data" tab
and click on "Sort."
c. In the sorting options dialog box,
define the first sort level (e.g., region).
d. Click "Add Level" to add a
second sorting level (e.g., product category).
e. Choose the sort order for each
level.
f. Click "OK" to apply the
multiple-level sorting.
Excel
Filtering for Focused Data Analysis:
Filtering
data in Excel allows you to display only the information that meets specific
criteria, effectively focusing your analysis on relevant data subsets. When you
have a large dataset with various categories, filtering helps you isolate
particular data points for closer examination.
To filter
data in Excel, follow these steps:
a. Select the range of cells that you
want to filter.
b. Navigate to the "Data" tab
on the Excel Ribbon.
c. Click on the "Filter"
button to enable filtering for the selected range.
d. Small drop-down arrows will appear
next to each column header.
e. Click on the drop-down arrow for the
column you wish to filter.
f. Choose specific criteria to display
or use search options to find specific data points.
g. Excel will show only the data that
meets your chosen criteria.
For
example, if you have
a dataset containing sales data for different products, you can use filtering
to show only the sales figures for a particular product category or
salesperson.
Excel
Advanced Filtering:
Excel's
advanced filtering feature allows you to apply multiple criteria
simultaneously, making it even more powerful for complex data analysis.
Advanced filtering helps you refine your data to gain deeper insights and
identify patterns that might not be immediately apparent.
To use
advanced filtering in Excel:
a. Ensure your data has headers for
each column.
b. Set up a criteria range with the
desired filter conditions.
c. Select the range of data you want to
filter.
d. Navigate to the "Data" tab
and click on "Advanced" in the "Sort & Filter" group.
e. In the advanced filtering dialog
box, specify the criteria range and choose whether to filter the data in place
or copy the filtered data to a new location.
f. Click "OK" to apply the
advanced filtering.
Clearing
Filters and Sorting:
After
filtering data, you might want to clear the filters to view the entire dataset
or change the sorting order. To clear filters, click on the filter drop-down
arrow and select "Clear Filter" from the list. If you need to modify
the sorting order, simply click on the column header again to toggle between
ascending and descending order.
Conclusion:
Excel's
sorting and filtering capabilities are indispensable tools for efficient data
management and analysis. Sorting enables you to organize data in meaningful
order, while filtering allows you to focus on specific data subsets for
in-depth analysis. Whether you're dealing with large datasets or looking for
specific insights, mastering these features in Excel empowers you to work with
data more efficiently and make informed decisions.
As you
continue your Excel journey, remember to experiment with sorting and filtering
on various datasets to familiarize yourself with their versatility. The ability
to arrange and analyze data with precision is a valuable skill that will prove
useful across various personal and professional endeavors.
So, harness
the power of Excel's sorting and filtering functions to take control of your
data and uncover hidden gems of insights. Happy data organizing and analyzing!