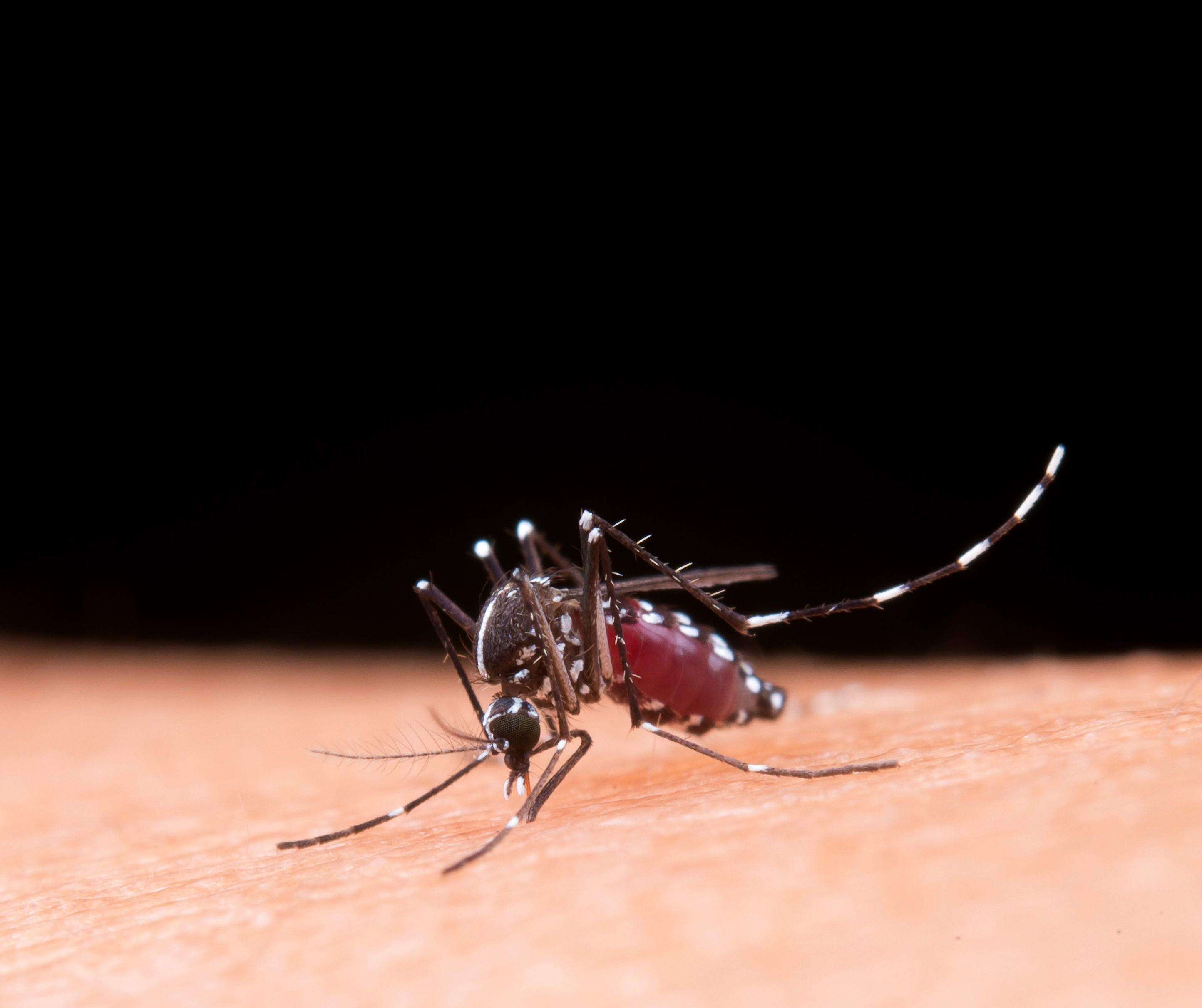
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne viral infection that is spread by the Aedes aegypti mosquito. The virus can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can be fatal in some cases.
Dengue fever is a major public health problem in tropical and
subtropical regions around the world. The World Health Organization (WHO)
estimates that there are 390 million dengue infections every year, and 96
million of those infections result in symptoms.
There has been a spike in dengue fever cases
worldwide in recent years. This is due to a number of factors, including:
·
Climate change: Climate change is making the environment
more favorable for mosquito breeding. Mosquitoes thrive in warm, humid
climates, and climate change is making these conditions more common.
·
Increased travel: People are traveling more than ever
before, and this is increasing the spread of dengue fever. When people travel
to areas where dengue fever is present, they can be bitten by infected
mosquitoes and bring the virus back home with them.
·
Urbanization: The world is becoming increasingly urbanized,
and this is creating more ideal conditions for mosquito breeding. Mosquitoes
breed in stagnant water, and there is more stagnant water in urban areas due to
things like poor sanitation and drainage.
The spike in dengue fever cases has led to a number of health concerns. In some cases, dengue fever can be fatal. In addition, the high number of cases is putting a strain on health care systems in many countries.
The symptoms of dengue fever usually start 4-10 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The most common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- Rash
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
In some cases, dengue fever can progress to a more severe form
called dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF). DHF is characterized by bleeding, low
blood pressure, and shock. If left untreated, DHF can be fatal.
There is no specific treatment for dengue fever. Treatment is
supportive, and includes rest, fluids, and pain medication. In severe cases,
hospitalization may be necessary.
The best way to prevent dengue fever is to avoid mosquito bites. This can be done by:
- Wearing long sleeves and pants
- Using insect repellent
- Sleeping under a mosquito net
- Eliminating mosquito breeding sites
If you are traveling to a tropical or subtropical region where
dengue fever is present, it is important to take steps to protect yourself from
mosquito bites. You can also talk to your doctor about getting vaccinated
against dengue fever.
Here are some additional facts about dengue fever:
- There are four different types of dengue viruses, and infection with one type does not protect you from the others.
- People who have been infected with dengue fever once are more likely to develop severe dengue if they are infected again.
- There is no cure for dengue fever, but most people recover completely.
- Dengue fever can be prevented by reducing mosquito breeding sites and using insect repellent.
If you think you may have dengue fever, it is important to see a
doctor right away. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing
complications.